Map reconstructing what Shoreham Harbour could have looked like in the 14th Century A.D. (It is ingenious rather than accurate.)
The Borough Seal featuring the 'hulc' , the most important trading vessel in Medieval times, is included in the bottom left.
The map shows Procession
Street running through what was reconstructed as the centre of the town.
Historians may query this as Procession Street is known as an important
peripheral street in medieval towns.
 |
Alluvial
muds which gives a good
indication of the route of the river and estuary in the past. Lagoons (like
the Widewater Lagoon) formed between the land
and the sea, but the coastline was not fixed and these would be altered
and washed away by the sea.
Below the top layer of alluvium
is a water-retaining sandy silt,
known as marsh clay. However, there is plenty of chalk
in the banks of the river, and this can be contrasted to the blue-grey
of the marsh clay. Alluvium is a general term for clay, silt, sand
and gravel. It is the unconsolidated detrital material deposited by a river,
stream or other body of running water as a sorted or semi-sorted sediment
in the bed of the stream or on its floodplain or delta.
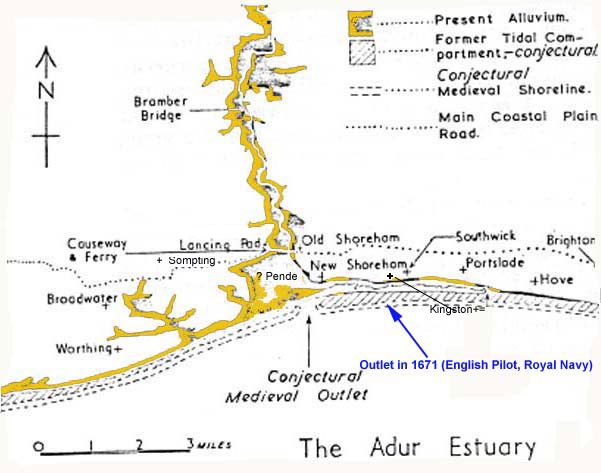
History of the Adur Estuary (by H. C. Brookfield 1950-1)
1671
John
Seller, The English Pilot (1671), the
second book, the first part, page 4, in summary:
Shoreham:
a tide haven, with 18 feet [on the bar at the mouth] at HWST, 3 feet at
LWST and LW common tides, 12 feet a HW common tides. The town is almost
a mile within the haven*.
Vessels drawing 8 to 9 feet can lie afloat at LW a little below the town,
but lie dry elsewhere. (At the
time of publication, this description may have already been out of date.)
[*This
would put the entrance at Silver Sands.]
Magic
Map Location of Pende (hypothesis)
Bramber Castle, now in ruins, was constructed by William de Braose about 1073. The initial fortification was an earthern motte, but later it was fortified with flint. (The date I have for a timber quay at Bramber is 1086).
William
de Braose's Calendarium Inquisit Post Mortem of 1094, which says:
'Shorham
maner et castr' de Bramber baronia
Brembre
maner et castr' extent' from
Simon
Stevens
The first bridge was wooden
(c. 1103) and the later stone bridge constructed over a substantial tidal
stream.
The date of the stone bridge
is not known, but it could have been built between 1180 and 1190. (London
Bridge started in wood, was rebuilt in stone in 1179). Two bridges over
the Adur at Bramber were definitely in existence in about 1230.
The foundation of the stone
bridge was of Sussex Marble (paludina limestone)
and the bottom course of cobbles (large pebbles from Shoreham
Beach).
The tidal inlet probably ran in two deep streams, the larger one on the western side.
Since then the reclamation of the tidal marshes, by a process called "inning", as well as a change in the coastline resulted in the silting up of the estuary. In 1232, floods could cause the bridge to be impassable.
In 1348 there is a church named St. Peter de Veteri Ponte, which may have been renamed St. Botolphs, in addition to a St. Peter church at Sele (Sele Priory), which is probably the church of St. Peter at Beeding.
In 1468, the stone bridge at Bramber (Between Bramber and Sele) is reported to be in bad repair.
By 1477-79, the deposition of silt was making navigation for sea going vessels under the Bramber Bridge impractical.
Sussex
Archaeological Society
Sussex
Archaeological Society EGroup